About
Developed through an innovative partnership with GitHub, the Digital Development Compass is UNDP’s latest tool supporting Member States with their inclusive digital transformation journeys. The Compass provides an analysis of a nation’s digital development based on a comprehensive collection of publicly available data sets.
The Digital Development Compass aggregates and synthesizes digital development indicators from over 140 open-source datasets into interactive dashboards. These dashboards cover the six pillars of the United Nations Development Programme's (UNDP) Digital Transformation Framework, allowing users to quickly understand the digital state of any nation.
In December 2025, the Digital Development Compass expanded to include a new component, the Digital Rights Dashboard, which reviews how countries are equipped to protect human rights online. The dashboard highlights how national contexts shape conditions to safeguard four key digital rights: freedom of expression, freedom of assembly and association, equality and non-discrimination, and privacy. It also includes cross-cutting factors that contribute to the broader enabling environment. Developed through extensive research across international law, UN documents, and global literature, the Digital Rights Dashboard is designed to support informed and context-aware dialogue on rights-based digital transformation.
Ultimately, the Digital Development Compass aims to serve as a guide and starting point for policymakers, practitioners and stakeholders in their efforts to promote digital development in their respective countries. The tool is not intended to be used as an evaluative statistical tool or an index. Users are encouraged to exercise caution and critical thinking when interpreting the results and to consider the broader socio-cultural, political and economic context of each country's digital development efforts.
Feedback and constructive criticism are welcome to improve the accuracy and usefulness of the Compass. To raise your concerns or reflections regarding the data or results, please contact us via the chatbox.
How the Compass works
The Compass provides a score that assesses a nation’s digital maturity. This is determined by the pillars of UNDP’s Digital Transformation Framework:
Each of these pillars consists of multiple sub-pillars and indicators, which can be mapped to a specific stage of digital transformation. Every stage is then assigned a score, which represents the level of a nation’s digital transformation maturity.
Let's walk through how to navigate the Compass:
Stages of digital readiness by transformation pillar
People
Overall
- Stage 1. Basic
- Limited exposure: Cultural aversion, minimal tech use.
- Stage 2. Opportunistic
- Limited literacy: Digital gap, basic use.
- Stage 3. Systematic
- Growing acceptance: Basic literacy, more complex tasks.
- Stage 4. Differentiating
- Technology embraced: Reduced gap, high literacy.
- Stage 5. Transformational
- Digital society: No gap, tech ingrained in society.
Skills and Literacy
- Stage 1. Basic
- Elite: Educated, skilled minority. Digital divide persists.
- Stage 2. Opportunistic
- Private: Basic skills, some schools, company training.
- Stage 3. Systematic
- Elective: Basic skills widespread, optional school learning.
- Stage 4. Differentiating
- Cultivated: Schools teach, tech equipped curriculum.
- Stage 5. Transformational
- Widespread: Universal skills, adult centers, industry shift, integrated education.
Usage and Adoption
- Stage 1. Basic
- Basic: Tech for leisure, low access and adoption.
- Stage 2. Opportunistic
- Transactional: Moderate use, gaps in access.
- Stage 3. Systematic
- Intermediate: Complex actions, info access, tech ownership.
- Stage 4. Differentiating
- Advanced: Complex services, reduced divide.
- Stage 5. Transformational
- Proficient: Comprehensive, universal access, reduced divide.
Culture Norms
- Stage 1. Basic
- Resistant: Low tech adoption, change incentives lacking.
- Stage 2. Opportunistic
- Tolerant: Tech as last resort.
- Stage 3. Systematic
- Accepting: Trial-error, active use, known channels.
- Stage 4. Differentiating
- Enthusiastic: Open, innovative, motivated tech adoption.
- Stage 5. Transformational
- Advocating: Full tech integration, societal reshaping.
Civic Engagement
- Stage 1. Basic
- Restricted: Tech not for citizen-govt interaction, voice exclusion.
- Stage 2. Opportunistic
- Volunteerism: Tech aids activism, accountability via volunteers.
- Stage 3. Systematic
- Community: Tech solves local issues, citizen decision influence.
- Stage 4. Differentiating
- Engaged: Tech shapes decisions, ethics guide communication.
- Stage 5. Transformational
- Participative: Integrated civic platforms, inclusive discourse, media outlets, encouraged participation.
Digital Public Infrastructure
Overall
- Stage 1. Basic
- Paper IDs, traditional payments, siloed data.
- Stage 2. Opportunistic
- Basic IDs, early digital payments, limited sharing.
- Stage 3. Systematic
- Digital IDs, mobile banking, online data sharing.
- Stage 4. Differentiating
- Integrated IDs, digital wallets, accessible data.
- Stage 5. Transformational
- Beneficial ID/banking, widespread payments, open data.
Payments
- Stage 1. Basic
- Traditional: Cash, checks dominate, rare digital payments.
- Stage 2. Opportunistic
- Changing: Digital access, cards, online banking, cashless.
- Stage 3. Systematic
- Systematic: Prepaid, mobile money, no bank account.
- Stage 4. Differentiating
- Differentiating: Decoupled payments, digital wallets.
- Stage 5. Transformational
- Transformational: Widespread digital payments, local currencies.
Identification
- Stage 1. Basic
- Paper-based: Birth, marriage, land records on paper.
- Stage 2. Opportunistic
- Digitized: Records digital, separate institutions.
- Stage 3. Systematic
- Digitalized: Machine-readable records, workflows set.
- Stage 4. Differentiating
- Integrated: Govt-business linked IDs, data protection.
- Stage 5. Transformational
- Federated: Inclusive system, citizens/businesses/entities.
Data Exchange
- Stage 1. Basic
- Offline: No data exchange, paper-based, no systems.
- Stage 2. Opportunistic
- Siloed: Limited exchange, spreadsheets, PDFs.
- Stage 3. Systematic
- Online: Central data, info systems, infrastructure.
- Stage 4. Differentiating
- Accessible: Governance, data use, decision-making.
- Stage 5. Transformational
- Open: Optimized model, public data, structured API.
Connectivity
Overall
- Stage 1. Basic
- Outdated connectivity, exclusion risk.
- Stage 2. Opportunistic
- Basic quality, limited access.
- Stage 3. Systematic
- Growing access, exclusion gaps.
- Stage 4. Differentiating
- Affordable, open access.
- Stage 5. Transformational
- Universal broadband, equal access.
Physical Infrastructure
- Stage 1. Basic
- Outdated: Limited coverage, unreliable infrastructure.
- Stage 2. Opportunistic
- Inaccessible: Basic quality, selective coverage.
- Stage 3. Systematic
- Rudimentary: Urban-focused high-speed coverage.
- Stage 4. Differentiating
- Convenient: Extended, reliable, majority covered.
- Stage 5. Transformational
- Extensive: Universal, high quality, reliable services.
Access Enablers
- Stage 1. Basic
- Blocked: Systemic barriers exclude at-risk groups.
- Stage 2. Opportunistic
- Restricted: Lower tech access, systemic barriers.
- Stage 3. Systematic
- Limited: Consistently lower access, ignored differentiation.
- Stage 4. Differentiating
- Open: Similar access, recognized barriers, free access points.
- Stage 5. Transformational
- Universal: Equal access, acknowledged barriers, full benefits.
Government
Overall
- Stage 1. Basic
- Limited: Paper bureaucracy, no funding, ad-hoc tech.
- Stage 2. Opportunistic
- Initiatives in silos, limited support, no strategy.
- Stage 3. Systematic
- Shared vision, limited funds, strategic planning.
- Stage 4. Differentiating
- Embedded, administrative integration, emerging tech.
- Stage 5. Transformational
- Optimized, innovative, legislative backing, data-driven.
Leadership and Strategy
- Stage 1. Basic
- Reactive: No strategy, no senior support, isolated projects.
- Stage 2. Opportunistic
- Informal: Scattered support, no national framework.
- Stage 3. Systematic
- Formal: Underdeveloped plan, moderate priority.
- Stage 4. Differentiating
- Strategic: Inclusive vision, some shared adoption.
- Stage 5. Transformational
- Visionary: Impactful strategy, top-level support, empowered leaders.
Implementation Capacity and Systems
- Stage 1. Basic
- Analogue: No skills, outsourcing, no strategy, no budget.
- Stage 2. Opportunistic
- Outsourcing: Few skills, external help, partial strategy.
- Stage 3. Systematic
- Digital seeds: Growing skills, some insourcing, developing strategy.
- Stage 4. Differentiating
- Integrated: Widespread skills, central strategy, metrics-driven.
- Stage 5. Transformational
- Digital by default: Embedded skills, centralized strategy, quantifiable objectives, long-term budget, full Digital Principles integration.
Digital Public Services and Platforms
- Stage 1. Basic
- Paper-based: No online services, in-person only.
- Stage 2. Opportunistic
- Digitization: Basic digital tools, in-person main.
- Stage 3. Systematic
- Digitalization: Online transactions, some redesign.
- Stage 4. Differentiating
- Integrated digitalization: Centralized, redesigned, data-centric.
- Stage 5. Transformational
- Smart State: Online access, optional in-person, full redesign.
Open Government
- Stage 1. Basic
- Closed: No info sharing, no feedback or evaluation.
- Stage 2. Opportunistic
- Reactionary: Limited sharing, key stakeholder input.
- Stage 3. Systematic
- Transparent: Regular info sharing, some stakeholder input.
- Stage 4. Differentiating
- Participatory: Info sharing, broad input, partial KPIs.
- Stage 5. Transformational
- Collaborative: Open, stakeholder partnership, robust feedback, evaluations.
Regulation
Overall
- Stage 1. Basic
- Initial stage. Non-digital laws apply.
- Stage 2. Opportunistic
- Formative: Digital laws developing.
- Stage 3. Systematic
- Established: Substantive digital laws, weak enforcement.
- Stage 4. Differentiating
- Advanced: Substantive laws, strong enforcement.
- Stage 5. Transformational
- Dynamic: Strong laws, justice, formal intl. cooperation.
Data and Privacy
- Stage 1. Basic
- No recognition: No data protection, access barriers.
- Stage 2. Opportunistic
- Regulate & forget: Ineffective legislation, no enforcement.
- Stage 3. Systematic
- Recognition: Functional data protection authority, regulation.
- Stage 4. Differentiating
- Promotion: Key data rights protected, enforced.
- Stage 5. Transformational
- Dynamic Legal Framework: Enforced tailored regulation, FOI used, accessible government data.
Emerging Technologies
- Stage 1. Basic
- No recognition: Tech not policy consideration.
- Stage 2. Opportunistic
- Regulate & forget: Uniform reg., no impact assessment.
- Stage 3. Systematic
- Recognition: Discuss need to regulate tech impact.
- Stage 4. Differentiating
- Promotion: Actively promotes growth, updates.
- Stage 5. Transformational
- Dynamic Legal Framework: Evolving, outcome-based, feedback loops, soft law mechanisms.
Fair Market Competition
- Stage 1. Basic
- No recognition: No IP law, static taxation, telecom monopoly.
- Stage 2. Opportunistic
- Regulate & forget: Outdated IP law, some competition.
- Stage 3. Systematic
- Recognition: Licensing promotes competition, balanced prices.
- Stage 4. Differentiating
- Promotion: Adaptive taxation, national IP protection.
- Stage 5. Transformational
- Dynamic Legal Framework: Anti-monopoly, IP protection, flexible dispute resolution.
Cybersecurity
- Stage 1. Basic
- No recognition: No cyber crime law, unprotected infrastructure.
- Stage 2. Opportunistic
- Regulate & forget: Developing law, seeking resources.
- Stage 3. Systematic
- Recognition: Enacted law, limited enforcement.
- Stage 4. Differentiating
- Promotion: Budget support, growing practice.
- Stage 5. Transformational
- Dynamic Legal Framework: Comprehensive law, baselines, compliance, international alignment.
Consumer Protection
- Stage 1. Basic
- No recognition: Digital service monopolies.
- Stage 2. Opportunistic
- Regulate & forget: Limited watchdog, partial monopoly.
- Stage 3. Systematic
- Recognition: Price monitoring, accessibility.
- Stage 4. Differentiating
- Promotion: Functional watchdog, diverse licenses.
- Stage 5. Transformational
- Dynamic Legal Framework: Strong watchdog, tailored legislation, price monitoring.
Human Rights
- Stage 1. Basic
- Not recognized: No digital human rights.
- Stage 2. Opportunistic
- Recognized: No action taken.
- Stage 3. Systematic
- Regulated: Focus on political rights.
- Stage 4. Differentiating
- Resourced: Legal resources, intl. standards.
- Stage 5. Transformational
- Fully protected: Legal, institutional, tech safeguards.
Economy
Overall
- Stage 1. Basic
- Limited integration: Traditional finance, low tech business.
- Stage 2. Opportunistic
- Growing tech: Digital finance, moderate tech business.
- Stage 3. Systematic
- Cross-sector collab: Seed financing, wide tech business.
- Stage 4. Differentiating
- Coordinated digital: Inclusive ecosystems, efficient tech.
- Stage 5. Transformational
- Digital industry: Responsibility standards, widespread models.
Business
- Stage 1. Basic
- Adverse: Limited tech adoption, unfavorable conditions.
- Stage 2. Opportunistic
- Developing: Moderate tech, sector-specific conditions.
- Stage 3. Systematic
- Favorable: Wide tech, improved conditions for all sectors.
- Stage 4. Differentiating
- Ecosystem formation: Majority use tech, coordinated policies.
- Stage 5. Transformational
- Ecosystem integration: Tech integrated, cooperative networks.
Financial Services
- Stage 1. Basic
- Emerging: Primarily physical access to financial services.
- Stage 2. Opportunistic
- Developing: Early adopters introduce basic digital services.
- Stage 3. Systematic
- Strategic: Established digital services, essential for finance.
- Stage 4. Differentiating
- Market leading: Mature digital financial services, market focus.
- Stage 5. Transformational
- People leading: Inclusive finance, public-private finance for the vulnerable.
Innovation Ecosystem
- Stage 1. Basic
- Stagnant: Limited graduates, outdated curriculum, lack of engagement.
- Stage 2. Opportunistic
- Emergent: Improved communication, industry-academia ties, updated curriculum.
- Stage 3. Systematic
- Siloed: Growing collaboration, international recognition.
- Stage 4. Differentiating
- Interconnected: Extensive engagement, cross-sector collaboration, international events.
- Stage 5. Transformational
- Dynamic: Thriving ecosystem, comprehensive collaboration, strong IT career path, global ties.
Standards Of Responsibility
- Stage 1. Basic
- Unaware: Lack of awareness about ethical standards in digital services.
- Stage 2. Opportunistic
- Cognizant: Awareness but limited action on ethical standards.
- Stage 3. Systematic
- Compliant: Minimum ethical compliance, external constraint view.
- Stage 4. Differentiating
- Practitioner: Accountability, privacy-centric design, transparency.
- Stage 5. Transformational
- Advocate: Embedded ethics, evolving standards, proactive advocacy.
A Digital Public Good
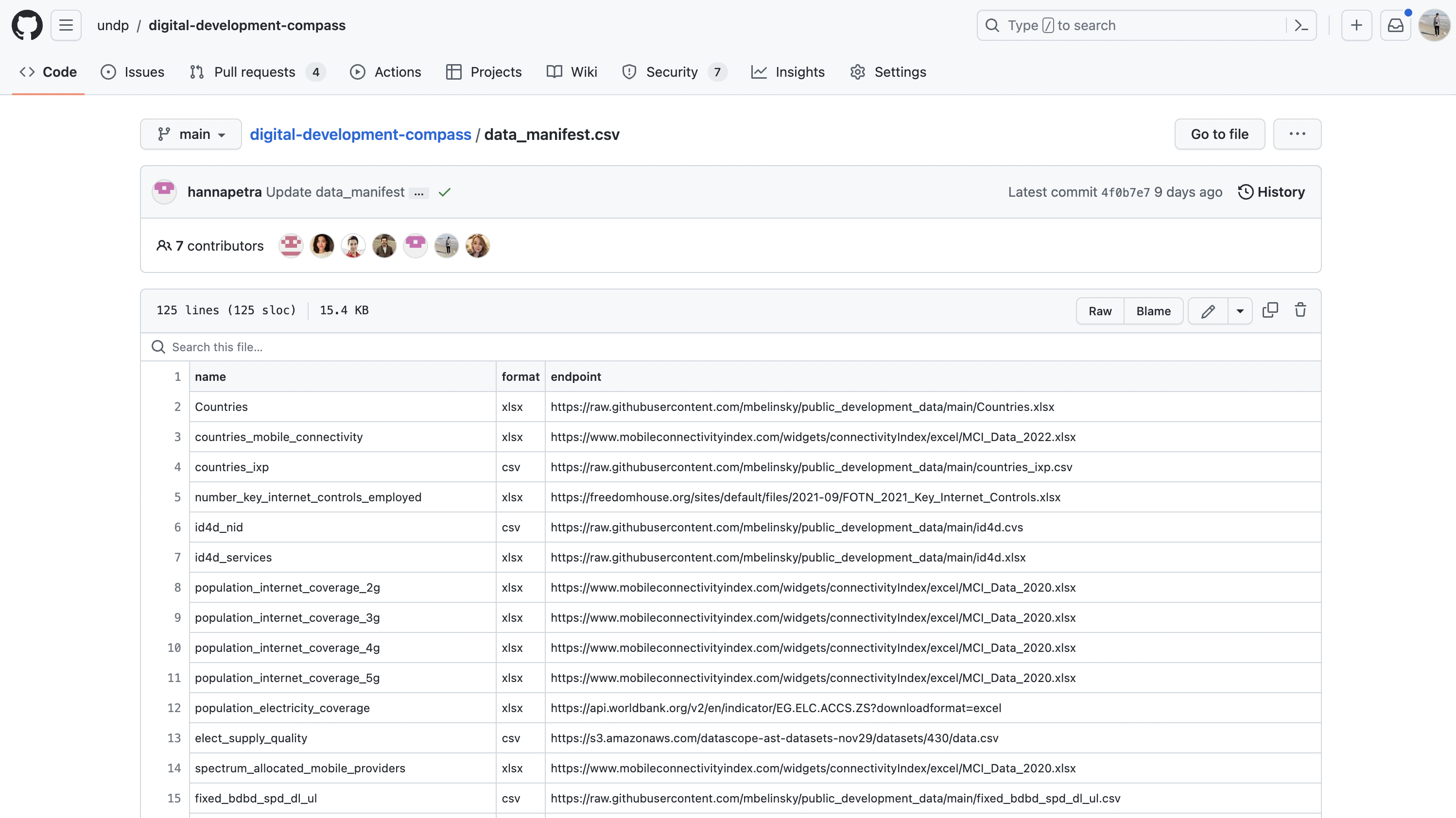
The software and data that are used to put together the Compass are open-source and in the process of becoming Digital Public Goods.
Automations scrape publicly available spreadsheets, PDFs, and documents, converting them into machine-readable formats. Scripts then normalize the data according to a UN-defined list of countries, regions, sub-regions, income groups and territorial borders. Data are also automatically updated as soon as international organizations release new reports. All code and data are transparent and available as a global resource on GitHub. Visit https://github.com/undp/digital-development-compass to see the latest.